Local Port Forwarding
When you want to access your MySQL database from home, but only have an ssh connection.
I find my self reading up this time and time again, I guess I do not do it often enough, so I decided to write this down atleast for my own, but perhaps there is someone else also in the need of this small example/tutorial, so let’s put it out on the internet for all to see.
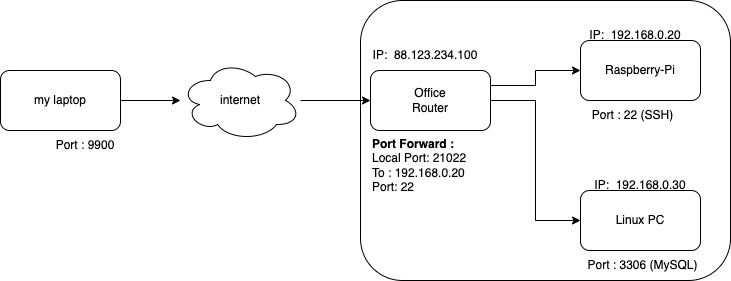
The example below intend to show how I can connect from my local laptop at home, to my office where an ssh connection has been allowed through a port forward in the Router to a machine (raspberry pi), and then I connect to a database on another machine in the same network. See picture below.
The ssh command looks like this
ssh -L 9900:192.168.0.30:3306 -p 21022 ssh-user@88.123.234.100
What the command does
ssh -L 9900:192.168.0.30:3306 -p 21022 ssh-user@88.123.234.100
- Connect to the Router at 88.123.234.100 (which is a public IP)
- The router listens on port 21022 , and will forward the connection to port 22 on 192.168.0.20 (which is the Raspberry Pi’s ssh server)
- The ssh server on the Raspberry Pi will forward the request once more to 192.168.0.30 (the Linux PC) on port 3306, which is the port of MySQL.
- Port 9900 is a local port on my laptop, and connecting my database client (e.g. dbeaver) to localhost:9900 will forward it to the MySQL process running port 3306 on 192.168.0.30
That is it !
/Tobias